
Ĭonventionally, only severely compromised and low Apgar scores have been regarded as predictive of maladaptive development and morbidity. A low Apgar score, commonly defined as a score of less than seven, has been associated with an increased risk of neonatal morbidity, mortality, and neurodevelopmental outcomes, such as motor, language, and educational outcomes. Generally, an Apgar score of seven or more at five minutes after birth indicates a newborn is adapting well to the environment, while a score of less than seven indicates complications.
#APGAR SCORE OF 6 PROFESSIONAL#
However, the Apgar score, particularly the five-minute Apgar score, is often used in outcome studies, as it provides useful clinical information about the fetal-to-neonatal transition, although some professional associations, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, encourage the use of the Apgar score only for its original intent.

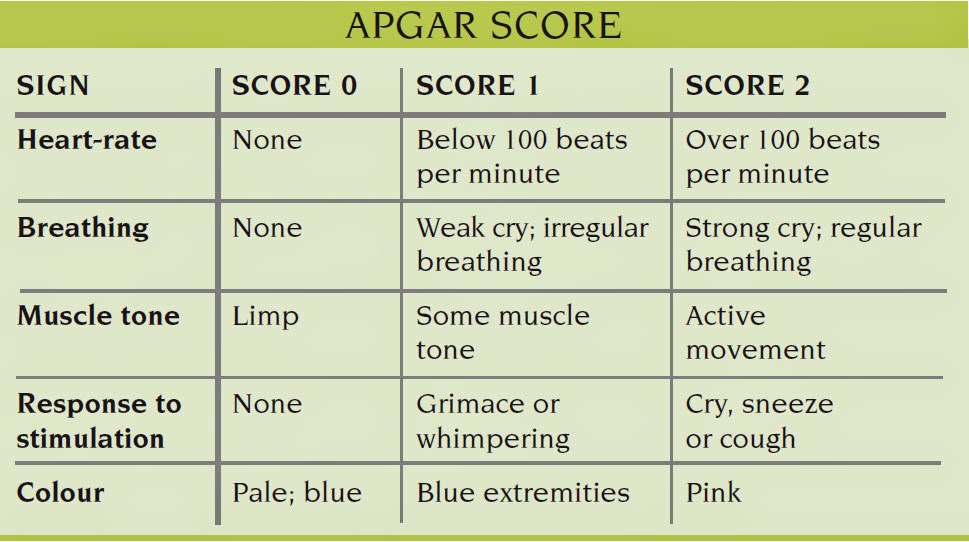
The Apgar score was originally intended to assess the condition of newborns immediately after birth and to measure the response to resuscitations. Compared with the one-minute Apgar score, the five-minute Apgar score is a better predictor of survival. Commonly, the Apgar score is measured at one minute and five minutes after birth and rated from zero to two points for each component, giving a total score that ranges from one to ten, where a higher score indicates better health and a greater chance of survival.
#APGAR SCORE OF 6 SKIN#
Hence, the Apgar score may need to be taken into account when evaluating neurodevelopmental outcomes in children.ĭeveloped by Virginia Apgar in 1952, the Apgar score has been used as a rapid assessment of the clinical condition of newborns based on physiological functions, such as respiration, heart rate, skin colour, muscle tone, and reflex irritability. Five-minute Apgar score was independently and inversely associated with a neurodevelopmental delay, and the risks were higher even within an Apgar score of 7−8. Further, when continuously modelled, the five-minute Apgar score was inversely associated with neurodevelopmental delay (AOR = 0.75 95% CI: 0.60, 0.93). Children with an Apgar score of 0−6 (AOR = 5.7 95% CI: 1.2, 27.8) and 7−8 (AOR = 4.1 95% CI: 1.2, 14.1) had greater odds of gross-motor neurodevelopment delay compared to children with an Apgar score of 10. Sixty-nine (8.5%) of children had a neurodevelopmental delay. Approximately 1.9% and 6.2% had Apgar scores of 0−6 and 7−8, respectively.

Of the 809 children, 614 (75.3%) had a five-minute Apgar score of 9, and 130 (16.1%) had an Apgar score of 10.
#APGAR SCORE OF 6 SOFTWARE#
Generalized estimating equations were used to model the association between the five-minute Apgar scores and neurodevelopmental outcomes, using STATA software V.15. Data from the Australian Longitudinal Study of Women’s Health (ALSWH) and Mothers and their Children’s Health (MatCH) study were linked with Australian state-based Perinatal Data Collections (PDCs) for 809 children aged 8−66 months old. This study aimed to evaluate the association of the five-minute Apgar score and neurodevelopmental outcomes in children by taking the entire range of Apgar scores into account.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
